What Is Reference/Payload Pattern?#
Instead of expecting users to know whether a complex asset requires payloading, many assets adopt the “reference-payload” pattern. This means their interface file is designed to be referenced, with the payload structure internal to the asset.
Important and inexpensive fields like variant sets and inherits are elevated above the payload when they are moved from the contents layer to the interface layer.
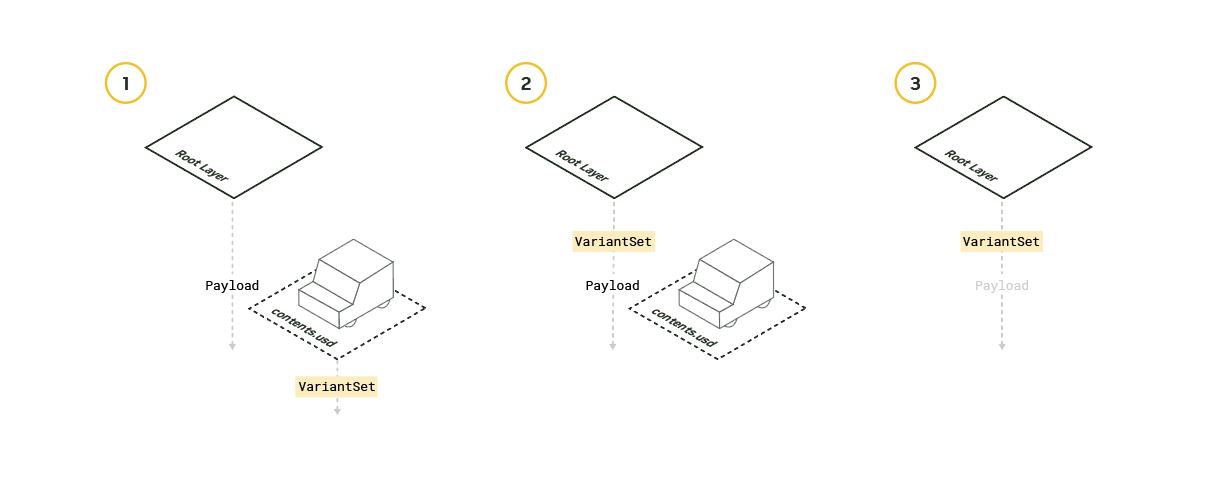
Lofting fields can help avoid the need to load a payload in certain contexts, thereby improving overall performance. Since there’s no general utility for lofting, it is typically achieved through site or project-specific post-scripts associated with asset generation and publishing. Fields found in the UsdModelAPI and UsdGeomModelAPI, such as extentsHint, are good candidates for lofting. The UsdGeomModelAPI provides a set of fields that enable the previewing of payloaded content before loading. Newer releases of OpenUSD have introduced the UsdMediaAssetPreviewsAPI as a schema for describing asset thumbnails.
By lofting fields, you are making functionality that was previously buried deep within the payload more accessible. This involves authoring new elements above the payload, creating overarching variant sets that control lower-level variant sets, and defining attributes that a payload connects to. Essentially, you are always introducing new fields and maintaining the accessibility of the functionality above the payload.
1# A lofted class does not contribute any opinions. It just provides a target for the arc.
2
3class "prop_MyAsset" {}
4
5def Xform "MyAsset" (
6 variantSets = ["color_variant"]
7 variants = {
8 string color_variant = "red"
9 }
10 payload = [@./contents.usd@]
11) {
12
13 # The lofted variants do not contribute any opinions.
14 # They just advertise the sets and selections specified by the underlying contents payload.
15
16 variantSets "color_variant" {
17 "red" {}
18 "blue" {}
19 }
20}
The references to the payload pattern can be used to recast a payload’s opinion ordering strength. While the example above uses an inline payload for brevity, if a mirroring resolver is used, it becomes important to keep the payload contents in separate layers.