Exercise: Adding an Export Option#
Previously, we added a core mandatory transformation step to our obj2usd converter to make it easier to reference our converted assets. End users may not want or need all of the available transformation steps. For this exercise, we will add a new transformation step in the form of an export option so that end users can choose whether to apply the transformation on conversion or not.
We will utilize the --up-axis command-line flag to allow end users to change the upAxis upon conversion to OpenUSD. This is desirable because even though OBJ is Y-up, the rest of an organization’s pipeline might be Z-up, and they would prefer that the output conforms to their pipeline.
Open
obj2usd.pyLet’s add a new function to handle this
--up-axisexport option and apply the transformation. Copy and paste this code betweenset_default_prim()andtransform():
1def set_up_axis(stage: Usd.Stage, up_axis: UpAxis):
2 """Set the specified up-axis for the stage.
3
4 OBJ is Y-up by default. This is an optional chaser to allow
5 users to change the up-axis to suit their pipeline. Corrective
6 transformations are applied.
7
8 Args:
9 stage (Usd.Stage): The stage to modify
10 up_axis (UpAxis): The up-axis value to set.
11 """
12 if up_axis == UpAxis.Y:
13 UsdGeom.SetStageUpAxis(stage, UsdGeom.Tokens.y)
14 else:
15 UsdGeom.SetStageUpAxis(stage, UsdGeom.Tokens.z)
16 xformable = UsdGeom.Xformable(stage.GetDefaultPrim())
17 xformable.AddRotateXOp(opSuffix="unitsResolve").Set(90.0)
This function sets the upAxis metadata accordingly. If the upAxis is not the OBJ default (Y), it will also apply a corrective on the defaultPrim to reorient the stage to remain face up in the new coordinate system. We suffix the X-axis rotation operation with “unitsResolve” by convention to explain to end users the purpose of the transformation.
This won’t do anything until we call the new function in transform().
Copy and paste this code into
transform():
1set_up_axis(stage, args.up_axis)
Click to reveal our Python code up to this point.
1import argparse
2import logging
3import math
4from enum import Enum
5from pathlib import Path
6
7import assimp_py
8from pxr import Gf, Sdf, Tf, Usd, UsdGeom, UsdShade
9
10logger = logging.getLogger("obj2usd")
11
12
13class UpAxis(Enum):
14 Y = UsdGeom.Tokens.y
15 Z = UsdGeom.Tokens.z
16
17 def __str__(self):
18 return self.value
19
20# ADD CODE BELOW HERE
21# vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv
22
23def extract(input_file: Path, output_file: Path) -> Usd.Stage:
24 logger.info("Executing extraction phase...")
25 process_flags = 0
26 # Load the obj using Assimp
27 scene = assimp_py.ImportFile(str(input_file), process_flags)
28 # Define the stage where the output will go
29 stage: Usd.Stage = Usd.Stage.CreateNew(str(output_file))
30 UsdGeom.SetStageUpAxis(stage, UsdGeom.Tokens.y)
31 # Assume linear units as meters.
32 UsdGeom.SetStageMetersPerUnit(stage, UsdGeom.LinearUnits.meters)
33
34 for mesh in scene.meshes:
35 # Replace any invalid characters with underscores.
36 sanitized_mesh_name = Tf.MakeValidIdentifier(mesh.name)
37 usd_mesh = UsdGeom.Mesh.Define(stage, f"/{sanitized_mesh_name}")
38 # You can use the Vt APIs here instead of Python lists.
39 # Especially keep this in mind for C++ implementations.
40 face_vertex_counts = []
41 face_vertex_indices = []
42 for indices in mesh.indices:
43 # Convert the indices to a flat list
44 face_vertex_indices.extend(indices)
45 # Append the number of vertices for each face
46 face_vertex_counts.append(len(indices))
47
48 usd_mesh.CreatePointsAttr(mesh.vertices)
49 usd_mesh.CreateFaceVertexCountsAttr().Set(face_vertex_counts)
50 usd_mesh.CreateFaceVertexIndicesAttr().Set(face_vertex_indices)
51 # Treat the mesh as a polygonal mesh and not a subdivision surface.
52 # Respect the normals or lack of normals from OBJ.
53 usd_mesh.CreateSubdivisionSchemeAttr(UsdGeom.Tokens.none)
54 if mesh.normals:
55 usd_mesh.CreateNormalsAttr(mesh.normals)
56
57 # Get the mesh's material by index
58 # scene.materials is a dictionary consisting of assimp material properties
59 mtl = scene.materials[mesh.material_index]
60 if not mtl:
61 continue
62 sanitized_mat_name = Tf.MakeValidIdentifier(mtl["NAME"])
63 material_path = Sdf.Path(f"/{sanitized_mat_name}")
64 # Create the material prim
65 material: UsdShade.Material = UsdShade.Material.Define(stage, material_path)
66 # Create a UsdPreviewSurface Shader prim.
67 shader: UsdShade.Shader = UsdShade.Shader.Define(stage, material_path.AppendChild("Shader"))
68 shader.CreateIdAttr("UsdPreviewSurface")
69 # Connect shader surface output as an output for the material graph.
70 material.CreateSurfaceOutput().ConnectToSource(shader.ConnectableAPI(), UsdShade.Tokens.surface)
71 # Get colors
72 diffuse_color = mtl["COLOR_DIFFUSE"]
73 emissive_color = mtl["COLOR_EMISSIVE"]
74 specular_color = mtl["COLOR_SPECULAR"]
75 # Convert specular shininess to roughness.
76 roughness = 1 - math.sqrt(mtl["SHININESS"] / 1000.0)
77
78 shader.CreateInput("useSpecularWorkflow", Sdf.ValueTypeNames.Int).Set(1)
79 shader.CreateInput("diffuseColor", Sdf.ValueTypeNames.Color3f).Set(Gf.Vec3f(diffuse_color))
80 shader.CreateInput("emissiveColor", Sdf.ValueTypeNames.Color3f).Set(Gf.Vec3f(emissive_color))
81 shader.CreateInput("specularColor", Sdf.ValueTypeNames.Color3f).Set(Gf.Vec3f(specular_color))
82 shader.CreateInput("roughness", Sdf.ValueTypeNames.Float).Set(roughness)
83 binding_api = UsdShade.MaterialBindingAPI.Apply(usd_mesh.GetPrim())
84 binding_api.Bind(material)
85
86 return stage
87
88
89def set_default_prim(stage: Usd.Stage):
90 """Set a default prim to make this stage referenceable
91
92 OBJ has no notion of a scene graph hierarchy or a scene root.
93 This is a mandatory chaser to move all prims under a default prim
94 to make this asset referenceable.
95 Args:
96 stage (Usd.Stage): The stage to modify
97 """
98
99 # Get the prim in the root namespace that we want to reparent under the default prim.
100 root_prims = stage.GetPseudoRoot().GetChildren()
101 world_prim = UsdGeom.Xform.Define(stage, "/World").GetPrim()
102 stage.SetDefaultPrim(world_prim)
103 editor = Usd.NamespaceEditor(stage)
104 for prim in root_prims:
105 editor.ReparentPrim(prim, world_prim)
106 editor.ApplyEdits()
107
108
109def set_up_axis(stage: Usd.Stage, up_axis: UpAxis):
110 """Set the specified up-axis for the stage.
111
112 OBJ is Y-up by default. This is an optional chaser to allow
113 users to change the up-axis to suit their pipeline. Corrective
114 transformations are applied.
115
116 Args:
117 stage (Usd.Stage): The stage to modify
118 up_axis (UpAxis): The up-axis value to set.
119 """
120 if up_axis == UpAxis.Y:
121 UsdGeom.SetStageUpAxis(stage, UsdGeom.Tokens.y)
122 else:
123 UsdGeom.SetStageUpAxis(stage, UsdGeom.Tokens.z)
124 xformable = UsdGeom.Xformable(stage.GetDefaultPrim())
125 xformable.AddRotateXOp(opSuffix="unitsResolve").Set(90.0)
126
127
128def transform(stage: Usd.Stage, args: argparse.Namespace):
129 logger.info("Executing transformation phase...")
130 set_default_prim(stage)
131 set_up_axis(stage, args.up_axis)
132
133
134def main(args: argparse.Namespace):
135 # Extract the .obj
136 stage: Usd.Stage = extract(args.input, args.output)
137 # Transformations to be applied to the scene hierarchy
138 transform(stage, args)
139 # Save the Stage after editing
140 stage.Save()
141
142# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
143# ADD CODE ABOVE HERE
144
145
146if __name__ == "__main__":
147 logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
148 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
149 "obj2usd", description="An OBJ to USD converter script."
150 )
151 parser.add_argument("input", help="Input OBJ file", type=Path)
152 parser.add_argument("-o", "--output", help="Specify an output USD file", type=Path)
153 export_opts = parser.add_argument_group("Export Options")
154 export_opts.add_argument(
155 "-u",
156 "--up-axis",
157 help="Specify the up axis for the exported USD stage.",
158 type=UpAxis,
159 choices=list(UpAxis),
160 default=UpAxis.Y,
161 )
162
163 args = parser.parse_args()
164 if args.output is None:
165 args.output = args.input.parent / f"{args.input.stem}.usda"
166
167 logger.info(f"Converting {args.input}...")
168 main(args)
169 logger.info(f"Converted results output as: {args.output}.")
170 logger.info(f"Done.")
Save the file and execute the script by running the following in the terminal:
Windows:
python .\data_exchange\obj2usd.py .\data_exchange\shapes.obj --up-axis Z
Linux:
python ./data_exchange/obj2usd.py ./data_exchange/shapes.obj --up-axis Z
Open the output USD stage with usdview to see the result:
Windows:
.\scripts\usdview.bat .\data_exchange\shapes.usda
Linux:
./scripts/usdview.sh ./data_exchange/shapes.usda
Click on “root” in the usdview tree view.
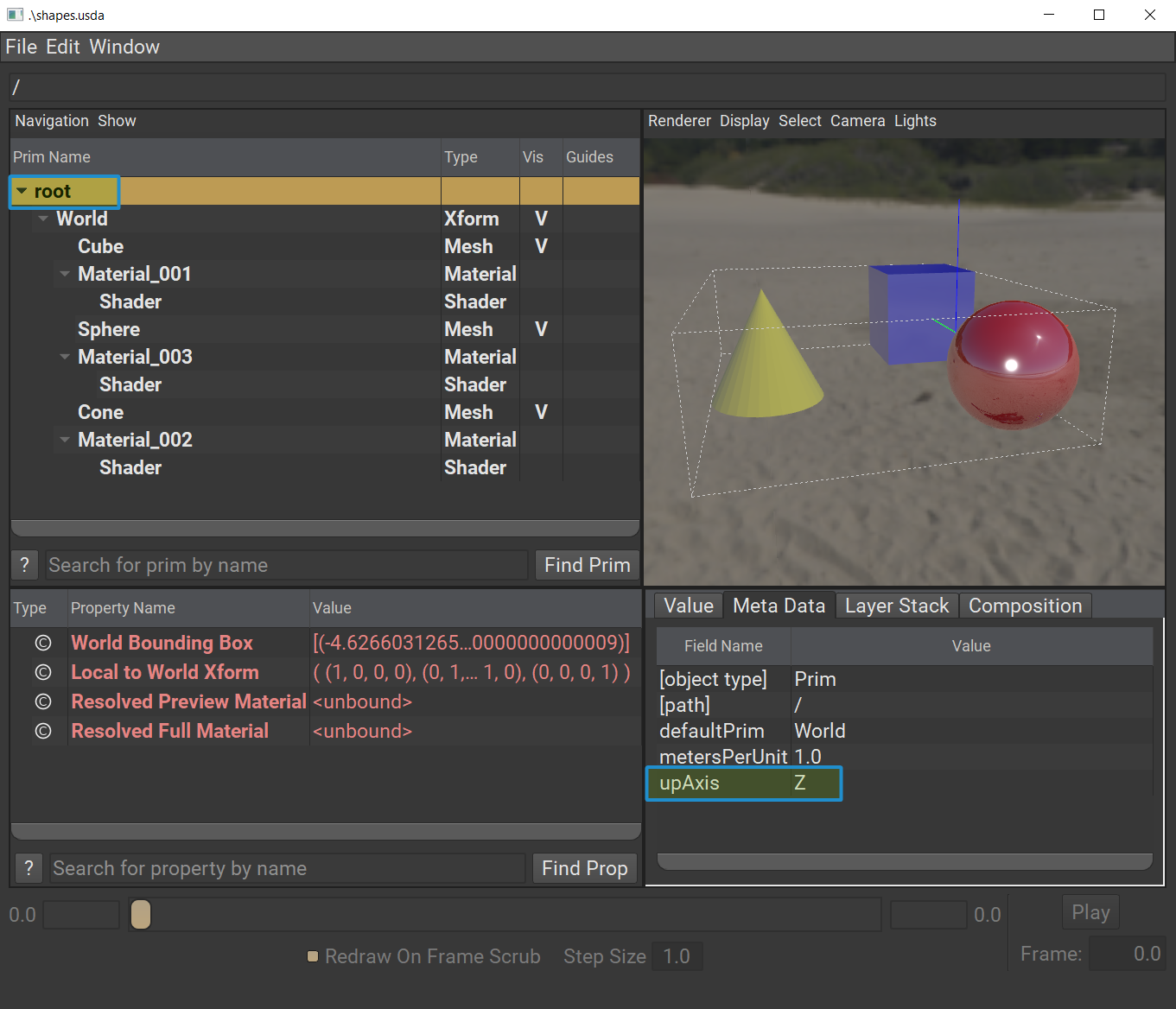
In the Meta Data tab, you can confirm now that upAxis is set to Z.
Click on “World” in the tree view.
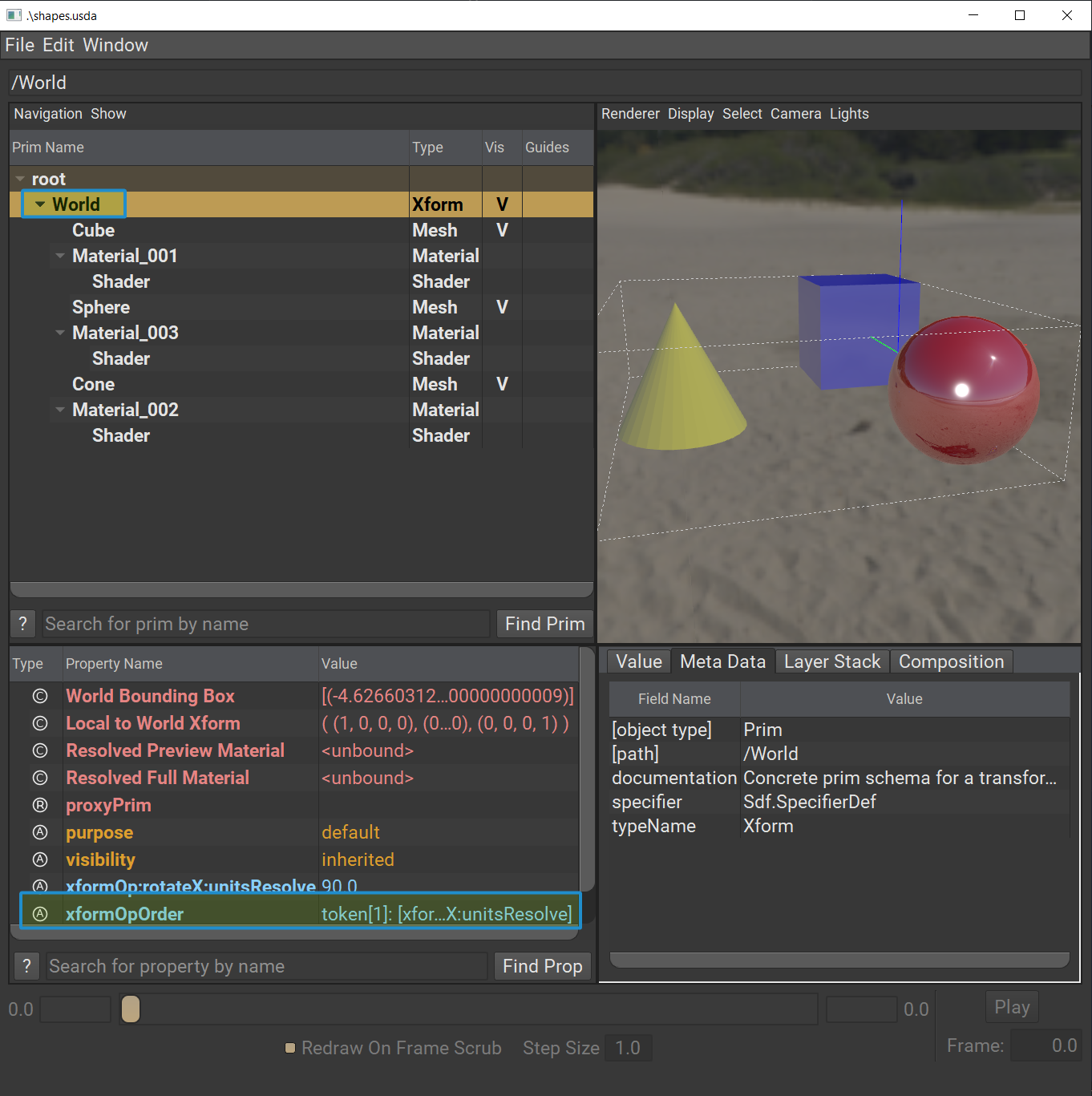
In the Properties panel, you can see the xformOp:rotateX:unitsResolve applying the corrective to keep the shapes upright despite the new upAxis.